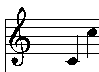Understanding musical theory
Welcome to kamatsu's article on Understanding Musical Theory.
The purpose of this article is to teach you:
- Basic Musical Notation
- Scales, Modes and Intervals
- Timing and Rhythmic Techniques
- Basic Harmony and Dissonance
- Chord Progressions
Contents
Scales, Keys, and Modes
The C Major Scale
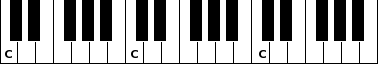
Music is made up of notes. Notes are sounds of a particular frequency (measured in hertz). Different frequencies produce different pitches. For the purposes of musical composition, we have culturally assigned particular names to different frequencies as we hear them, usually letters. C, for example, is the note produced when you play the white key before a group of two black keys on a keyboard.
Note: You will notice that C occurs every 8 notes on the keyboard. Why is this? The notes are separated by a specific distance of frequencies called an octave, and, for those that know the physics, the frequencies are logarithmically compatible, so that playing them together will sound like the one note. This means that for almost all purposes they can be treated as effectively the same note. Try it, if you have access to a keyboard. You will hear that they sound the same, just with different stylised pitch.
On a Musical score (with a treble clef), we see C as one of these two notes (usually):
From this point, one can easily deduce the names of the other white key notes:
If you play the white keys on the keyboard, starting at C (C, D, E, F..) you will hear a distinctive sequence of notes that most people recognize as the major scale (Do, Re, Mi, Fa...). If you have no idea what a major scale sounds like, here's a recording:
( link "Link Here" formerly at http://kamatsu.spheredev.org/majorscale.ogg : OGG of C major scale )
This is a major scale in the key of C. That means, Do, or the tonic, is C. Later on, we'll learn how to change the tonic. Here's what a full C Major scale looks like in Musical Notation (with a treble clef):
Extra Info: Think of a melody, say, your national anthem. Then, change the note at which you start the melody. Can you still sing/play it? You should quickly realize that it doesn't actually matter what note you start on, or what note Do is, for a melody to be recognizable to the human ear. Most humans think of notes relative to each other, not relative to specific frequencies. So, you could sing the Major scale at any pitch, from A through G#, and it would still be a major scale. But, if you start playing a piano from D, and play all the white notes up to the next D, it doesn't sound like a major scale (it's actually a dorian scale). So, obviously, simply shifting all the notes up a line or space in the Notation isn't going to achieve a D Major scale. How do you achieve this? Well, first, we need to learn about semitones, and then keys.
Clefs
A clef is a sign that is put at the beginning of a line of notation (a staff - plural staves), that determines what each line represents pitch-wise. On a treble clef, the note on the line below the bottom line of the staff (i.e, Do:C in the above diagrams) represents a specific note called Middle C (so called because it is in the middle of a piano keyboard). In the Bass clef, Middle C is on the line above the top line of the staff.
Mnemonics for Treble Clef: Suppose you want to be able to immediately identify a note name from looking at a staff (a useful skill). Having a mnemonic or verse to help you remember what each line and spaces stands for is quite useful. Here's the mnemonics for the treble clef.
- For lines (starting at the bottom and going up) - Every Good Bolshevik Deserves Freedom. Or, less politically, Every Green Bus Drives Fast. Your choice.
- For Spaces (Starting at the bottom space and going up) - F A C E - It spells "FACE", or, alternatively, you can use: Free Alcohol Can Entice. Once again, your choice.
While for the most part in this article we will be using notation in the treble clef, the most common clef, some scores may be written in the bass clef. The Bass Clef is more suited to lower ranges.
Mnemonics for remembering the bass clef:
- Lines (starting at the bottom and going up) can be remembered by "Good Boys Deserve Free Alcohol".
- Spaces can be remembered by "All Cows Eat Grass."
Intervals, Tones, and Semitones
If you examine a keyboard:
You will quickly see that there are no black keys between E and F, and B and C. Even more importantly, some of you may be wondering what those black keys actually represent. Between most lettered notes (C, D, E...) there is another note. This note is named relative to the notes it is adjacent to, so the black key between C and D would be called C Sharp (C♯) or D Flat (D♭), depending on your point of reference. The interval between notes is the distance pitch-wise between them. The interval from C to D is called a tone. The distance, therefore, from C to C♯/D♭ is a semitone - half a tone.
Note: The interval between E and F, as well as B and C is not a tone as you would expect but a semitone. That is why there is no black key between these notes. As a corollary of this, E♯ is therefore the same note as F, and B♯ is the same note as C (And C♭ = B, and F♭ = E). If you listen carefully to the major scale recording I played earlier, and you have a good musical ear, you may be able to hear the difference in the interval on these notes. An octave is another type of interval. We will learn more about intervals later in the introduction to harmony.
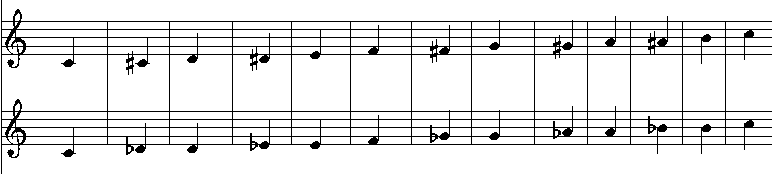
Now that we have learnt about semitones, we can develop a chromatic scale. A chromatic scale is a scale that goes up by a semitone each interval. Here's a chromatic scale in musical notation.
Note: The first staff uses sharps to notate the semitones, whereas the second staff uses flats. They produce the same tune.
As with before, you can listen to the chromatic scale produced by the above staves below:
( link "Link Here" formerly at http://kamatsu.spheredev.org/chroma.ogg : OGG of chromatic scale )
Notice how we start and finish the scale on the same two notes (an octave apart) that we see from the Major Scale, however we fit a helluva lot more notes in?
Compositional Tip: Moving chromatically in a piece can add a chaotic, tense element to your sound. Note however that chromatic music is very difficult to write well, so wait until you're fairly experienced.
Extra Info: Notating sharps or flats in this fashion - next to the notes that are modified - is called accidental notation. If you apply an accidental to a note, that accidental will apply for the rest of the bar to all notes on the line or space on which the accidental occurs. A bar is a way of grouping notes according to time, and they are separated by long vertical lines (as we see in the above staves). We will learn more about bars, barlines, as well as the natural symbol after we have covered keys and time signatures.